Structure of Mutual Funds in India

In India, the structure of Mutual Funds is a three-tier structure with a few other significant components. It is not just the different banks or AMCs that create or float different mutual fund schemes; instead, there are other players that are involved in the structure of mutual funds. The primary watchdog in all these transactions is the Securities Exchange Board of India (‘SEBI’) under whom each entity is required to be registered with. The inception of SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996, revolutionized the structure of mutual funds and since then all the entities are regulated under it. Currently, mutual funds comprise of five basic participants, namely a Sponsor, Mutual Fund Trustee, Asset Management Company, Custodian & Registrar and a Transfer Agent.
The Hierarchy looks like this:
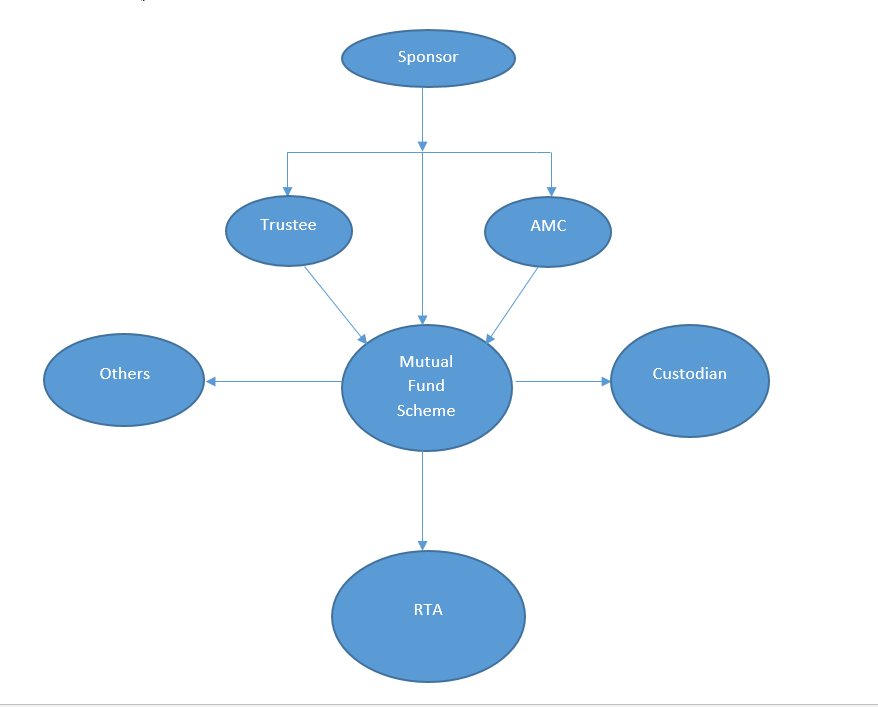
Sponsor
A sponsor is any person or entity that can set up a mutual fund scheme to generate income through fund management. The sponsor can be said as the first layer of the three-tier structure of mutual funds in India. The sponsor is required to approach SEBI and get a mutual fund scheme approved. The sponsor cannot work alone. It needs to create a Public Trust under the Indian Trust Act 1882 and get the same registered with SEBI. Once the trust is created, the Trustee is registered with SEBI and is appointed as the trustee of the fund in order to safeguard the interest of the unit holders and to adhere the SEBI Mutual Fund regulations. The Sponsor subsequently creates an Asset Management Company under the Companies Act, 1956 to deal with the fund management. There are certain eligibility criteria to become a Sponsor, as prescribed under:
a. The Sponsor must have profit in 3 of the last 5 years including immediately preceding year.
b. The Sponsor must have a minimum of 5 years of experience in financial services.
c. The net worth of the Sponsor must be positive for all the preceding five years.
d. Out of the total net worth of the AMC, 40% must be participated by the Sponsor.
As seen above, the position of a Sponsor is crucial and they should have high credibility. Strict norms show that the sponsor must have enough liquidity and faithfulness to return the money of an innocent investor, in case of a financial meltdown.
Trust and Trustees
Trust and trustees make up the second layer of the structure of mutual funds. Trustees are also known as the protectors of the fund and are employed by the fund sponsor. As the name suggests, they have a very important role in maintaining the trust of the investors and to oversee the growth of the fund. SEBI mandates the trustees to provide a report on the fund and the functioning of the AMC on a half-yearly basis. Trustees can be created either in the form of Board of Trustees or a Trust Company. The Trustees supervise the entire functioning of the AMC and regulate the operations of the mutual fund schemes. The SEBI has tightened the rule of transparency so as to avoid any conflict of interest between the Sponsor and the AMC. Without the permission and approval of the Trust, an AMC cannot float a new mutual fund scheme. It is important for the Trustees to act independently and take appropriate measures to safeguard the hard earned money of the investors. The Trustees are also required to be registered under SEBI, and SEBI further regulates their registration by either suspending or revoking the registration if found breaching any conditions.
Asset Management Company
An AMC is the third working layer in the structure of mutual funds. An AMC floats various schemes of mutual fund in the market, pursuant to the needs of the investors and the nature of the market. They create mutual funds along with the trustee and the sponsor and then oversee its development. While creating the scheme, they take help of bankers, brokers, RTAs auditors etc. and enter into an agreement with them. An AMC is a company formed under Companies Act and needs to be registered under SEBI. Similar to the Trustees, an AMC also needs to ensure that there is no conflict of interest amongst them, the sponsor and the trustees.
Other Participants in the Structure of Mutual Funds
Custodian
A Custodian is an entity, which is responsible for the safekeeping of the securities. Custodians are registered with SEBI and are responsible for the transfer and delivery of units and securities. Custodians also enable investors in updating their holdings at a particular point of time and help them in keeping track of their investments. Along with the primary job of safekeeping, custodians are also in charge of the collection of corporate benefits such as bonus issue, interest, dividends etc.
Registrar and Transfer Agents
RTAs are an important link between fund managers and investors. They cater to the fund managers by updating them with the investor details and to investors by delivering the benefits of the fund to them. RTAs are SEBI registered entities who process the applications of mutual funds, help with investor KYC, manage and deliver periodical statements of investments, update records of investors and process investor requests. Link-in time, Karvy etc. are some of the famous RTAs in India and they provide the requisite operational support to the AMC in mutual fund activities.
Other Participants
Some other participants in the structure of mutual funds are brokers, auditors, and bankers. The brokers are responsible to attract investors and help to disseminate the fund. The brokers help investors in sell, purchase of units and provide with their valuable advice. Brokers also study the market trend and predict the future movement of the market. Unlike brokers, auditors are an independent internal watchdog, who audit the financials of the AMC, Trustee, and Sponsor and provide their report. Bankers are also an important participant, who act as collecting agents on behalf of the fund managers.
These are the participants who play a key role in the management of mutual funds. Each participant has their individual role to play. However, their functions are interlinked with each other. Mutual fund regulations are the bible by which all the participants are bound together, to perform their functions more diligently and without prejudice to the interest of the investors.


No Comments